Description
What is Pig Pigging?
The term “pigging” refers to the use of devices known as “pigs” or “Pipeline Inspection Gauges” to perform various tasks within pipelines. These tasks include cleaning, inspecting, and maintaining the interior of pipelines. Developed in the mid-20th century, the term “pig” was originally an acronym for “Pipeline Inspection Gauge”. The early devices used in the process made a squealing noise while traveling through the pipeline, which is how they got their name.
What is the Purpose of Pigpigging?
The process of pig pigging is crucial for maintaining pipeline integrity and ensuring the efficient flow of fluids, including oil, gas, and water. Pigs are used to remove debris, rust, and other contaminants from the pipeline walls, reducing the risk of corrosion and blockages which could otherwise lead to significant operational issues and costly repairs. For instance, the failure of a major pipeline due to corrosion or blockage could result in significant environmental damage and financial losses.
Types of Pigging Pigs
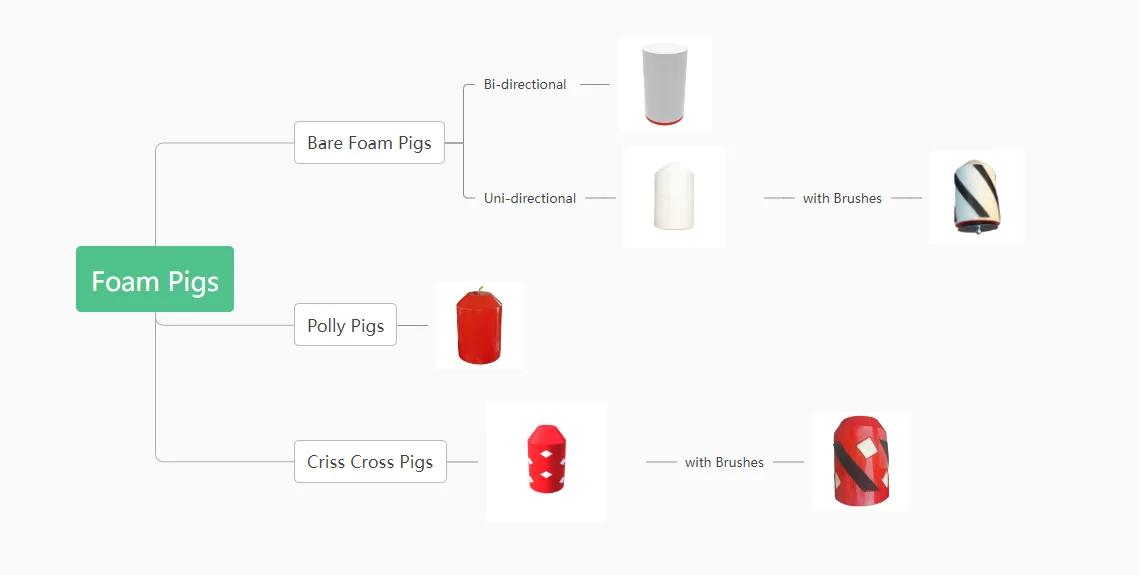
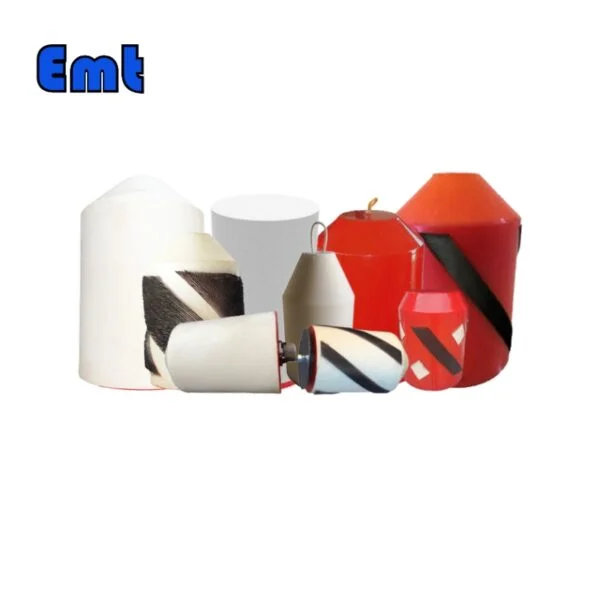
Foam Pigs
Foam pigs, like Bare Foam pigs, Polly pigs, and Criss Cross pigs, are key to keeping pipelines clean. Bare Foam pigs, made from light foam, are great at getting rid of loose dirt and fluids. Polly pigs, made of a special kind of foam called polyurethane and sometimes wrapped in a spiral pattern or fitted with wire brushes, are really good at removing tough build-ups or rust. Crisscross pigs, with their unique design, are excellent at tackling hard-to-remove dirt. Some foam pigs even have brushes, making them even better at cleaning. Each type of foam pig is created with certain pipeline conditions and cleaning needs in mind, ensuring the best results and a well-maintained pipeline.
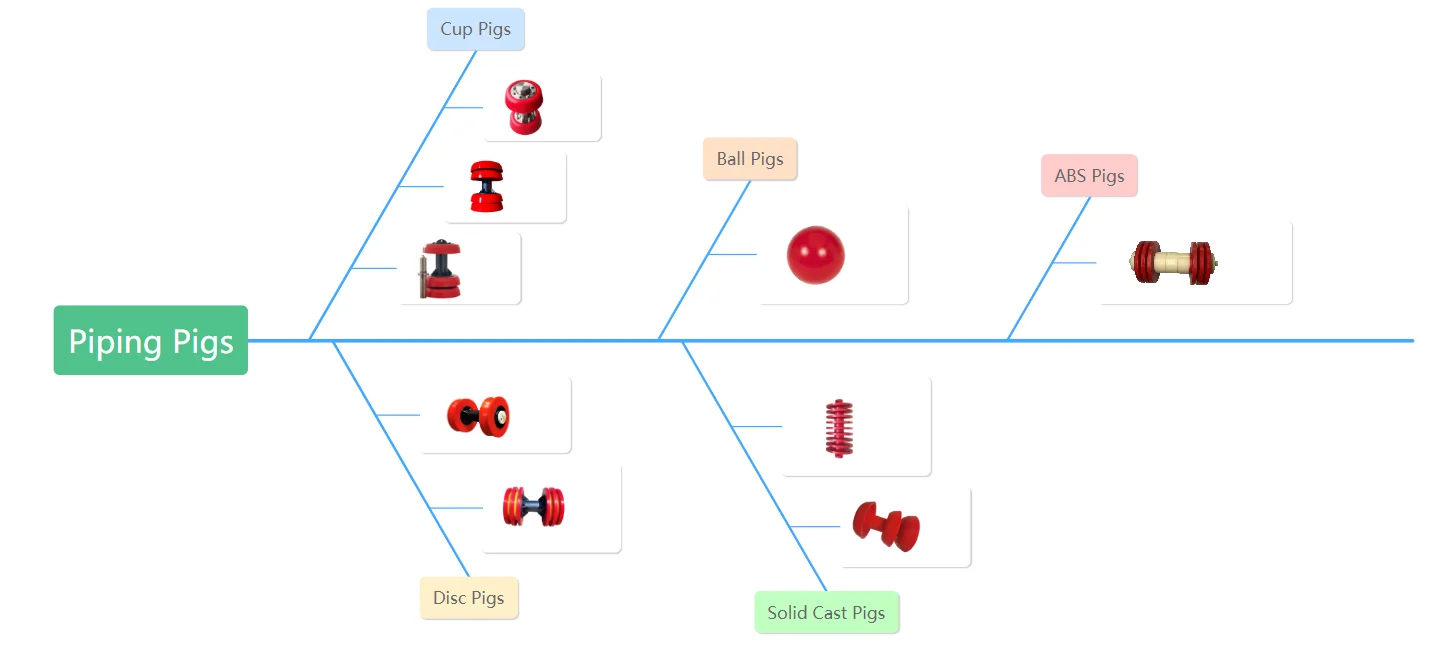
Piping Pigs
Apart from foam pigs, there are also several other types of pigs utilized in pipeline maintenance, each with their unique design and purpose.
Cup pigs are designed with flexible cups that form a seal against the pipeline wall. This not only helps to remove debris and fluids but also allows the pig to traverse bends and fittings with ease.
Disc pigs, on the other hand, are equipped with stiff discs that provide a scraping action, making them effective at removing more tenacious deposits.
Ball pigs are simple and versatile, their spherical shape allowing them to move smoothly through the pipeline while displacing unwanted materials.
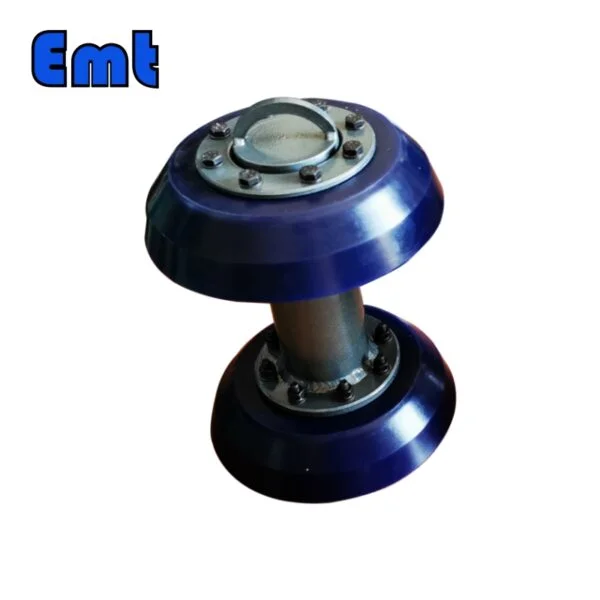
Solid cast pigs are robust and durable, often used for heavy-duty applications where tough deposits need to be removed.
ABS pigs, made from Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, a type of thermoplastic, are known for their strength and resilience, making them suitable for a wide range of pipeline cleaning applications.
Each of these pig types plays a specific role in pipeline maintenance, thereby ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of the pipeline system.
How Does Pig Piging?
Pigs are inserted into a pipeline at a designated point known as a “pig launcher” and are propelled by the flow of the product, such as oil or gas, to a receiving point called a “pig receiver” or “pig trap”. Pigs can be designed for specific tasks, such as cleaning or inspecting, and are equipped with sensors to monitor the condition of the pipeline. For example, “smart pigs” are equipped with advanced tools and sensors that can measure wall thickness, find small cracks, and detect other potential problems in the pipeline.
What is the Procedure for Pipeline Pig Pigging?
The pigging process involves inserting the pig into the launcher, which is then closed and pressurized to start the pig moving. As the pig travels through the pipeline, it pushes out debris and collects valuable data about the interior conditions of the pipeline. Operators monitor the pig’s progress and analyze the collected data to identify and address issues within the pipeline. It’s noteworthy that in some cases, pigs may get stuck or lodged within the pipeline. In such instances, procedures are in place to locate and retrieve the pig, minimizing disruption to pipeline operation.
 The Importance and Benefits of Pigging
The Importance and Benefits of Pigging
Pigging offers immense benefits to the operation of pipelines, playing a significant role in both their efficiency and safety.
Efficiency: Pigging ensures the smooth flow of substances in the pipeline. By removing debris, rust, and other contaminants, it helps to maintain the pipeline’s carrying capacity. Without regular pigging, deposits can build up inside the pipeline and slow down the flow of oil, gas, or water. In extreme cases, these deposits can even cause blockages, leading to operational downtime and costly repairs. By keeping the pipeline clean, pigging helps to prevent such issues and ensures the efficient transportation of substances.
Safety: Pigging also contributes to the safety of pipeline operations. Debris and rust in pipelines can lead to corrosion over time, weakening the structural integrity of the pipeline. This could potentially result in leaks or even catastrophic failures, posing a risk to both people and the environment. Pigging helps to mitigate this risk by removing the corrosion-causing elements. Moreover, inspection pigs or “smart pigs” can detect issues like cracks or thinning walls early on, allowing operators to address these problems before they escalate.
One specific example of a problem that pigging has helped to prevent is pipeline ruptures. Pipeline ruptures can lead to massive environmental disasters, especially when carrying hazardous substances like oil. Regular pigging, especially using smart pigs, helps to identify potential weak spots in the pipeline, allowing for preventive maintenance and reducing the risk of such incidents.
Summary
This article provides an in-depth look at the process of pigging in pipeline maintenance. It starts by defining pigging as the use of devices called “pigs” or “Pipeline Inspection Gauges” which are crucial for cleaning, inspecting, and maintaining pipelines. The article then explores the different types of pigs, including foam pigs and other types like cup pigs, disc pigs, ball pigs, solid cast pigs, and ABS pigs. Each type has unique designs and purposes, geared towards specific pipeline conditions and cleaning needs. The process of pigging is explained, where pigs are inserted into a pipeline at a point known as a “pig launcher” and are propelled to a “pig receiver” or “pig trap”. The pigs push out debris and collect valuable data about the pipeline’s interior conditions.
The article emphasizes the importance and benefits of pigging, which contributes significantly to the efficiency and safety of pipeline operations. It ensures a smooth flow of substances, prevents build-ups, and mitigates risks of leaks or failures. The use of pigging to prevent pipeline ruptures, a potential environmental disaster, is highlighted as an example of its importance. In conclusion, pigging plays a critical role in pipeline operations, contributing to their efficiency, safety, and overall success.

 The Importance and Benefits of Pigging
The Importance and Benefits of Pigging




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.