Description
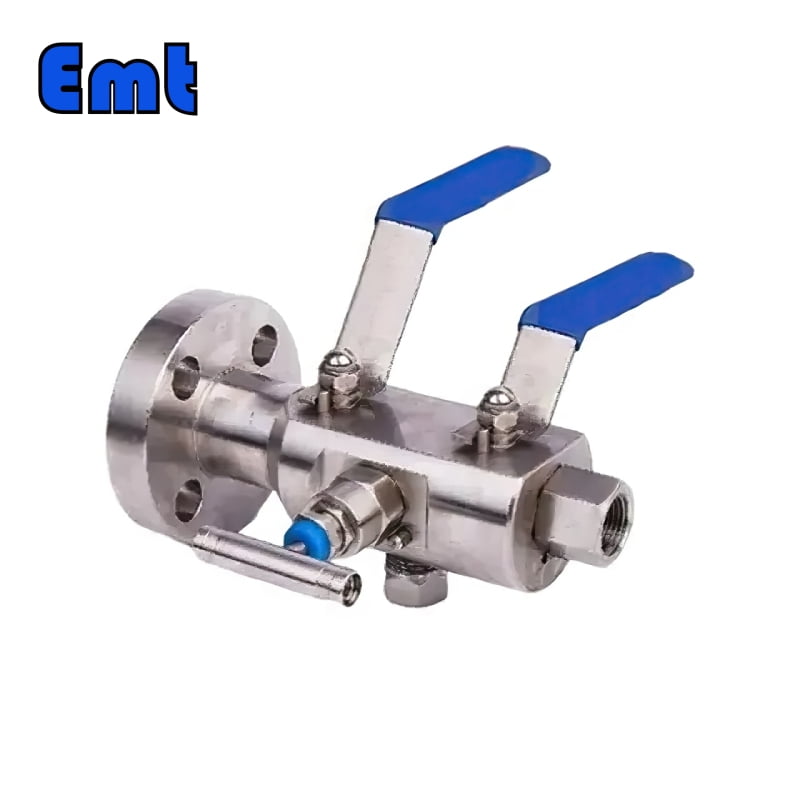
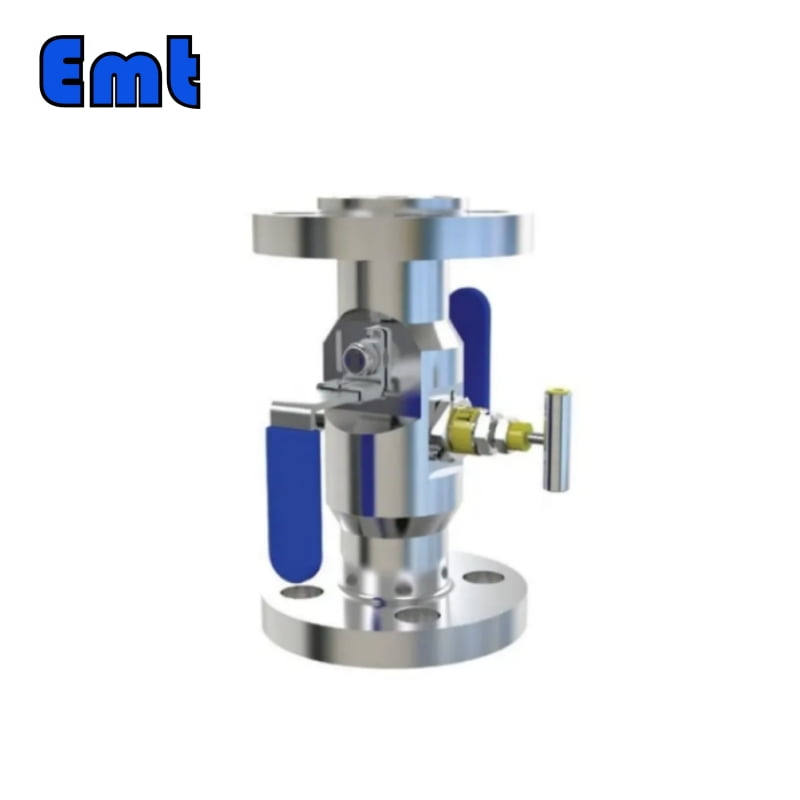
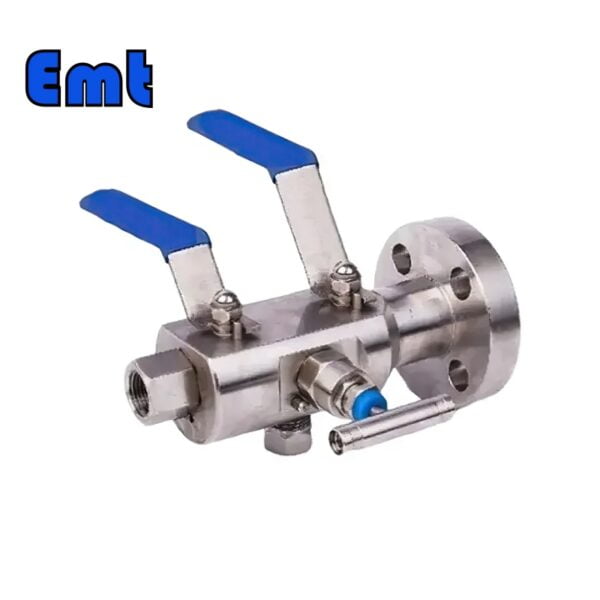
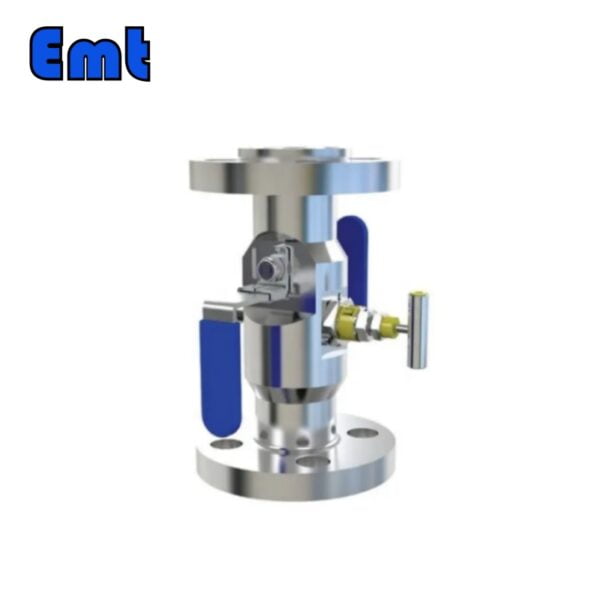
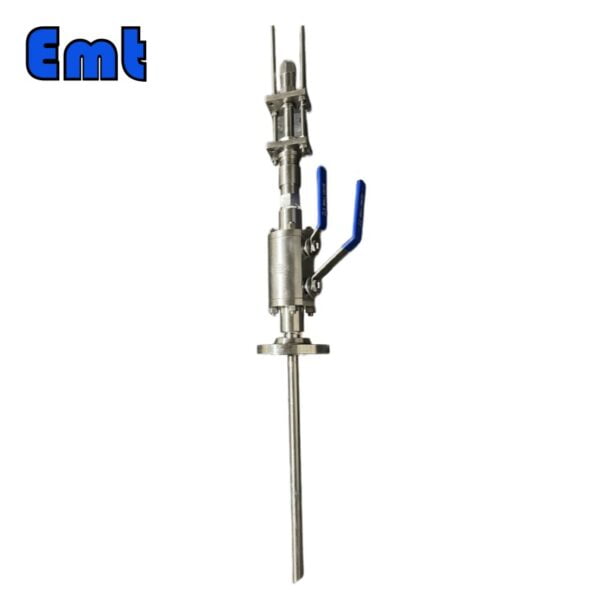
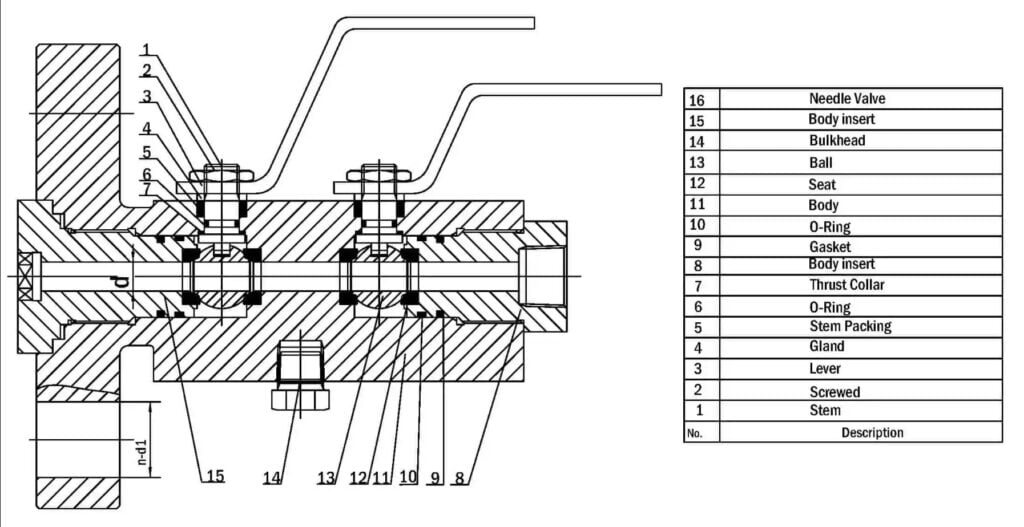
Double plug discharge valves, commonly referred to as DBB valves, are an indispensable part of modern industrial processes. It cleverly combines two isolation valves and one exhaust valve into a single product, providing a compact and efficient solution for safe fluid handling. DBB valves are widely used in chemical injection tubes and pig signalers, providing reliable isolation performance, reducing installation and component costs, and minimizing problems caused by vibration. From oil and gas fields to petrochemical and pharmaceutical plants, DBB valves continue to play a key role in improving operational efficiency and safety.
Parameters of the DBB Valve
| Name | High-Pressure Pipeline Chemical Injection DBB Valve |
| Material | Stainless Steel 304 or Stainless Steel 316 |
| Operating Temperature | 54-640°C |
| Features | 1. Easy to Operate |
| 2. Cost-effectiveness and versatility | |
| 3. Long life and high efficiency | |
| Payment | TT/FC |
| Advantages | 1. The reduction in installation and component costs can lead to savings of up to 70%. |
| 2. Costs associated with installation and components can be reduced by up to 70%, leading to significant savings. | |
| 3. Minimized vulnerability to issues stemming from vibrations. |
The Mechanics of DBB Valve
A. The Role of the Two Isolation Valves
The two isolation valves in the DBB valve are the main components that provide the “double blocking” function. These isolation valves are located on either side of the exhaust valve and are designed to safely block the flow of process fluids. When the two isolation valves are closed, they form a safe barrier that prevents any fluid from passing through. This is especially beneficial during maintenance or system shutdown, ensuring the safe isolation of process fluids.
B. The Function of the Bleed Valve
The exhaust valve is located between the two isolation valves and plays a key role in safely venting or discharging the cavity formed when the two isolation valves are closed. The exhaust valve allows any trapped process fluid to be safely drained or vented, ensuring that the pipe section can be safely opened for maintenance or inspection without the risk of pressurized release of the process fluid.
C. The Process of Isolation and Bleeding
The process of isolation and bleeding with a DBB valve involves a series of steps. First, the two isolation valves are closed to form a blockade of the process fluid. Next, open the air valve to drain or discharge the trapped fluid in the cavity between the isolation valves. This process ensures that the section of the pipe is completely isolated and free of process fluids, making it safe for maintenance or inspection work. When the work is complete, close the exhaust valve and then open the isolation valve to resume the flow of process fluids.
Comparisons and Considerations
A. Comparing DBB Valves with Traditional Valve Systems
DBB valves offer significant advantages over conventional valve systems. Unlike traditional systems, which require multiple valves for isolation and bleeding, DBB valves consolidate these functions into a single unit. This makes DBB valves more compact, efficient and economical. DBB valves also provide a higher level of safety by providing a double blocking function that ensures complete isolation of process fluids.
In contrast, a DIB valve, while similar to a DBB valve, offers double isolation, meaning it can seal the process flow from both directions. This makes the DIB valve particularly useful in situations where it is necessary to ensure that fluid cannot flow through either side.
B. Factors to Consider When Selecting a DBB Valve
There are several factors to consider when choosing a DBB valve.
Application: Consider where and how the valve will be used. Different applications may require specific types of DBB valves.
Material: Consider the type of fluid the valve will handle. Some fluids may require a valve made of a special material to withstand corrosion or other chemical reactions.
Pressure and temperature: Check the rated pressure and temperature of the valve. Make sure they match the operating conditions of the valve.
Diameters: DBB valves have different diameters. Choose a pipe that works for you.
Cost: While DBB valves can save money over time, they can cost more upfront. Make sure initial and long-term costs are taken into account.
Differences between the DBB Valve and the DIB Valve
DBB Valves:
DBB valves usually have two isolation valves and one exhaust valve. The main function of the DBB valve is to isolate or block the flow of fluid in the system so that it can be safely maintained or tested. In DBB valves, the two isolation valves provide a double barrier that ensures no fluid passes through, while the exhaust valve allows the space between the two isolation valves to be drained or vented.
DIB Valves:
DIB valves, on the other hand, provide double isolation, but in a different way. DIB valve has two isolation functions, one is to isolate the upstream pressure, the other is to isolate the downstream pressure. Each isolation valve in the DIB valve can provide its own isolation. This means that the two sides of the DIB valve can be pressurized independently of each other.
The DIB valve has a two-direction sealing capability, which is particularly useful in applications that ensure that fluid cannot pass through the valve in both directions. For example, DIB valves can be used in situations where you do not want a potentially dangerous fluid upstream to mix with another fluid downstream, and vice versa.
Although DBB valves and DIB valves look similar, their differences make them suitable for different applications. Therefore, it is necessary to understand these differences in order to choose the right valve for your specific needs.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.