Description
Understanding the DBB Valve
A Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valve is a specific type of valve used primarily in the oil and gas industry, but also in various other industrial applications. The main purpose of a DBB valve is to stop the flow of fluid and to ensure the complete isolation of fluid in a system.
Types of DBB Valves
DBB valves indeed come in two primary designs: the Modular or Split Body Type and the Integral Type. Understanding each design’s unique features and applications will help you select the best DBB valve for your needs.
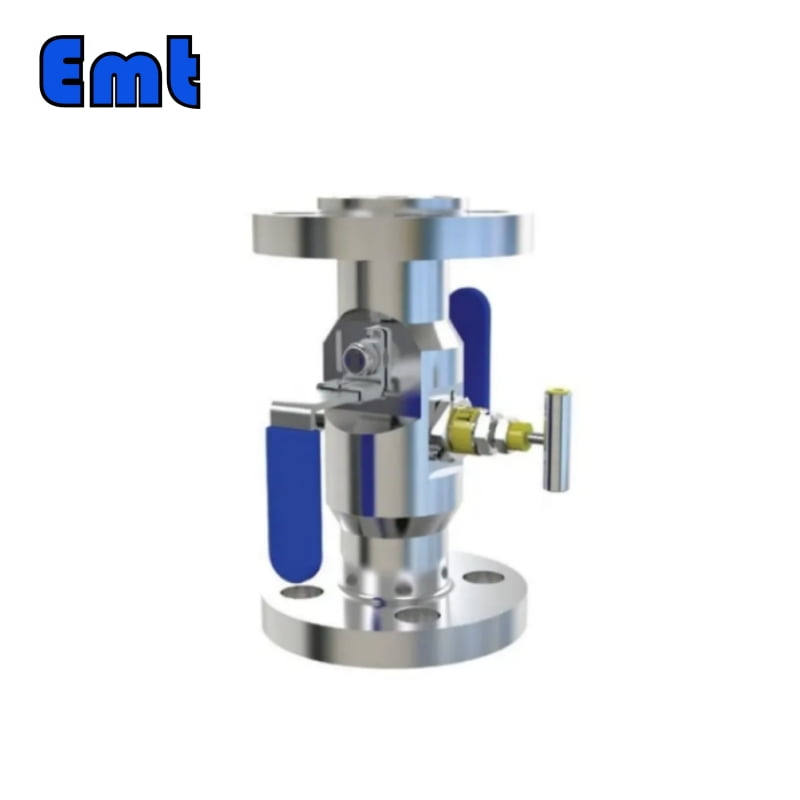
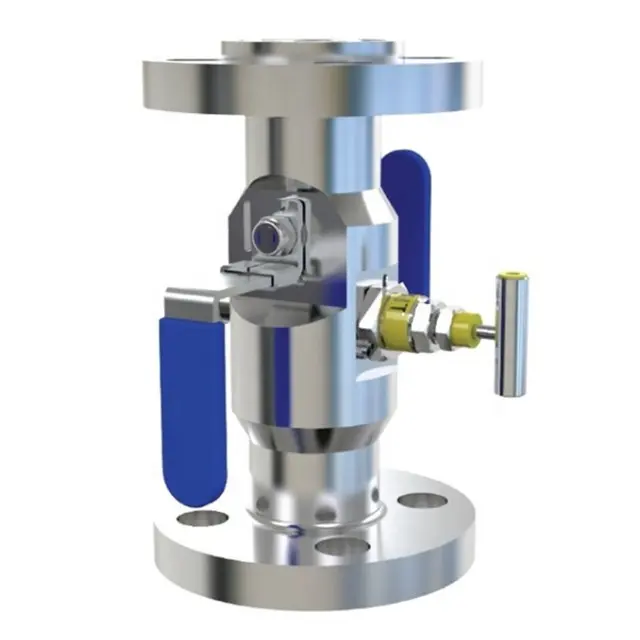
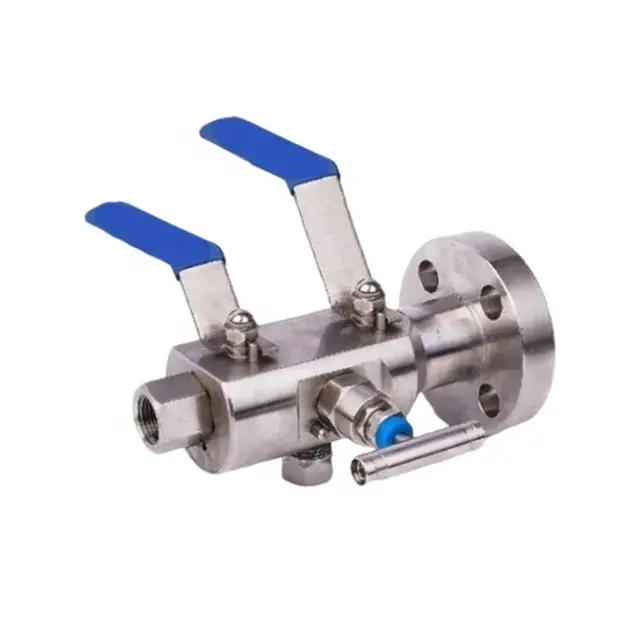
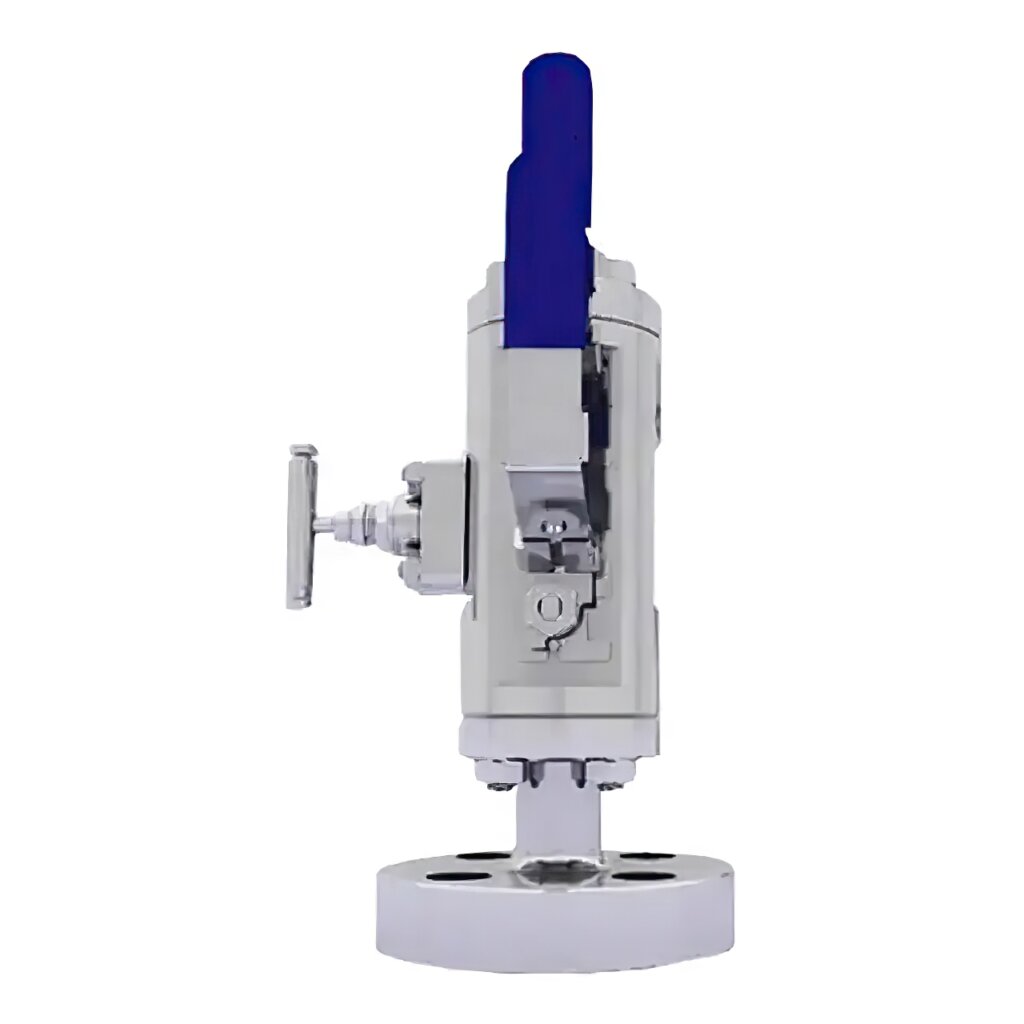
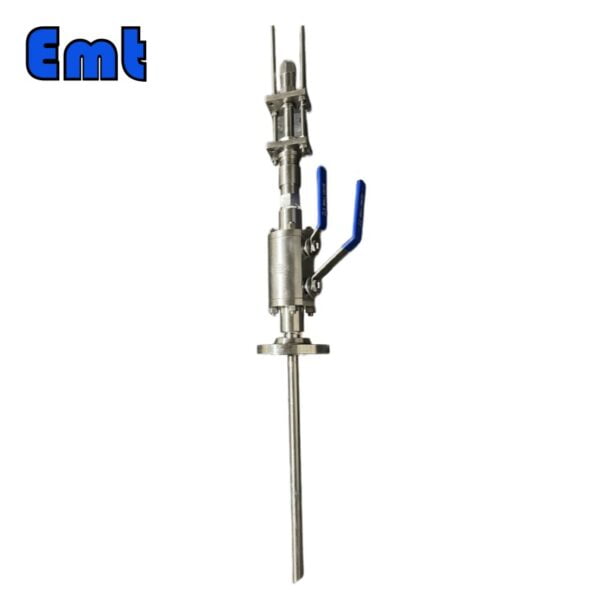
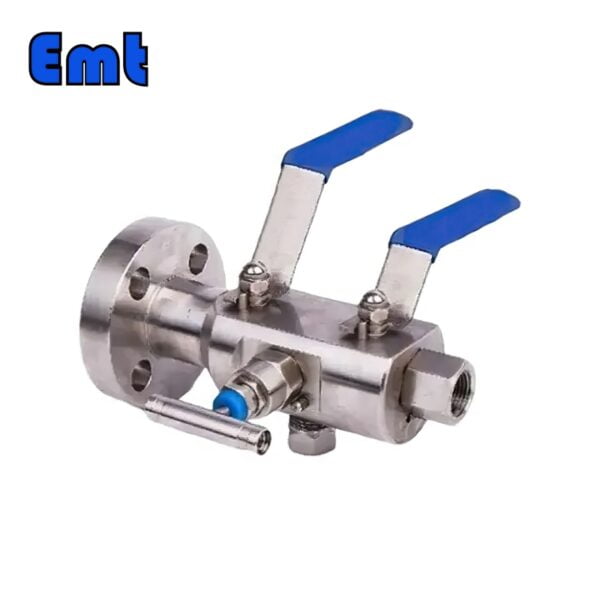
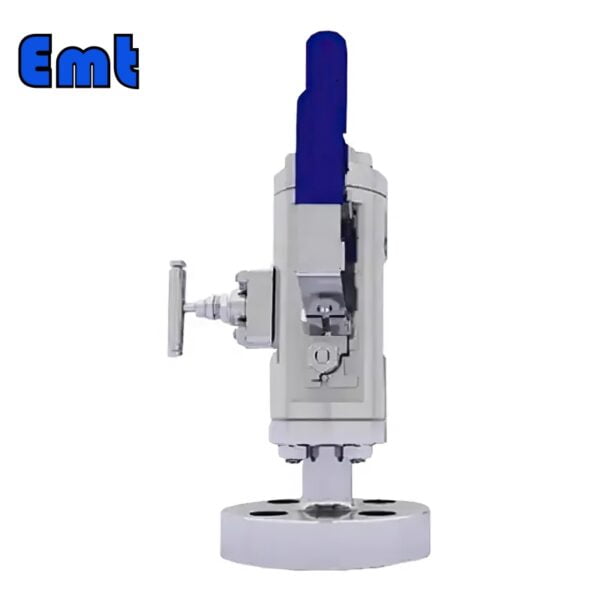
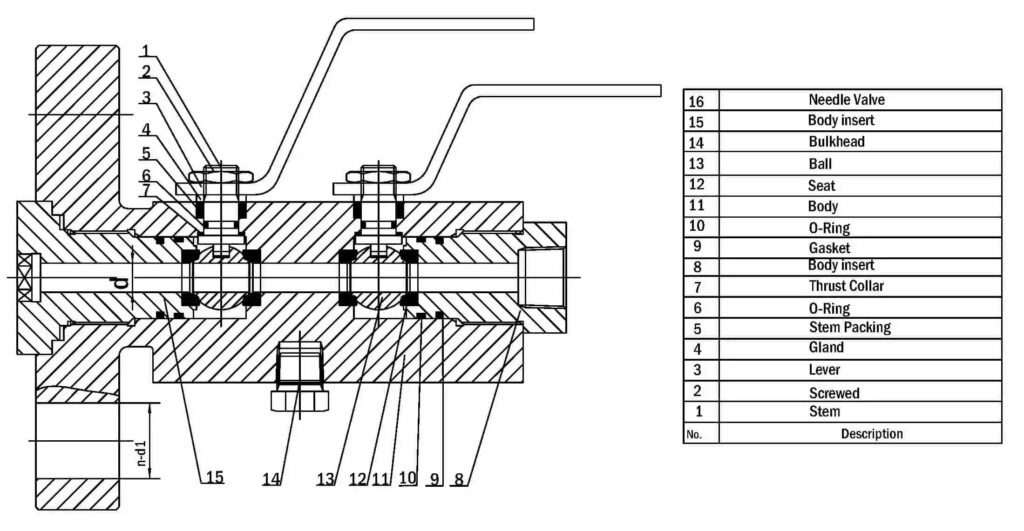
- Modular or Split Body Type DBB Valve: This design is characterized by its dual-ball structure, providing an extra layer of safety. The presence of two balls in a single valve body guarantees a double blockage, a critical feature in high-risk applications. A key component of this design is the drain needle valve, strategically situated between the two balls. This valve facilitates the draining of the valve, enabling the pressure to be reset to zero when needed. This design’s modularity, facilitated by its three-piece body construction, makes it versatile and beneficial for numerous applications, including instrumentation and piping. These valves come in a variety of sizes, ranging from 1 to 24 inches, and can handle an array of pressure class ratings, from API 3,000 to API 10,000, and in all pressure class scores from 150 to 2,500 lbs.
- Integral DBB Valves: These valves, primarily utilized in the instrumentation industry, come in a plethora of designs to cater to a wide range of needs. Designs include flange-to-flange, flange-to-thread, injection and sampling, and ball and needle types, offering flexibility for diverse industrial applications. Similar to the Modular or Split Body Type, the Integral DBB also features a drain needle valve positioned between the two balls. This allows for the draining of the valve and the resetting of the pressure to zero when required. The integral design is known for its robust construction and the ability to efficiently handle pressure.
How to Choose the Right DBB Valve
Selecting the appropriate Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valve for your needs requires a thorough understanding of the application, the type of medium being controlled, and the operational conditions, particularly temperature and pressure. Let’s delve deeper into each of these factors:
- Nature of the Application: The specific requirements of your application play a pivotal role in determining the appropriate DBB valve. For instance, if you need to maintain the integrity of a system while repairing a section of the pipeline, a DBB valve can provide the necessary isolation. In such a scenario, you may employ two gate valves to block the onstream flow. Meanwhile, a ball valve can be utilized to vent the fluid from the blocked pipeline section, allowing repairs to occur safely. Understanding the intricacies of your application can guide you toward the most suitable DBB valve type and configuration.
- Type of Medium: The type of medium, or media, that you intend to control also greatly influences the selection of a DBB valve. For controlling viscous liquids and dense gases, for example, you might need a full-bore ball, globe, or gate valve as a block valve due to their capacity to handle these types of media. A needle valve, known for its precision, is often chosen as a bleed valve in such situations. If dealing with corrosive media, it might be necessary to opt for stainless steel DBB valves, which offer excellent resistance to corrosion, ensuring the media is effectively blocked without causing any damage to the valve itself.
- Operational Temperature and Pressure Conditions: The conditions under which your operation is carried out will also affect your choice of DBB valve. High-pressure, high-temperature applications might necessitate the use of anti-static ball valves as block valves. These types of valves are engineered to withstand pressure fluctuations and vibration, making them safe for use in sensitive operations. In contrast, low-pressure operations might be better suited to a single DBB gate valve with adjustable wedges and a body bleed valve, which can offer the required functionality without the need for high-pressure resistance.
By considering these factors – the nature of the application, the type of medium, and the operational conditions – you can make an informed decision when selecting a DBB valve, ensuring that it will meet your specific needs and contribute to the safe and efficient operation of your system.
Advantages of Using DBB Valves
Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valves are ingeniously designed to replace the traditional method of joining individual valves together to achieve dual isolation. This streamlined design offers several significant benefits:
- Space, Weight, and Installation Efficiency: DBB valves consolidate multiple valve functions into a single unit, leading to substantial savings in terms of weight and space—up to 60% in some cases. This compact design is especially advantageous for insulating instruments or instrument cages. Furthermore, by simplifying the number of components to be installed, DBB valves can also reduce installation time by up to 70%.
- Environmental Safety: One of the standout advantages of DBB valves is their potential to minimize environmental impact. By significantly reducing the number of potential leak paths, DBB valves decrease the likelihood of hazardous leaks, enhancing the overall safety of your operations.
- Maintenance Safety: When maintenance tasks need to be performed downstream of the first isolation valve, dual isolation is crucial. DBB valves fulfill this requirement perfectly. They feature either a ball or a globe vent valve that allows for safe venting of the pressure trapped between the two isolation valves.
- Versatility and Added Functions: DBB valves have evolved to include additional functions such as chemical injection and sampling points, further increasing their utility. Some designs even integrate control valves, making these multi-functional valves a versatile choice for various applications.
In essence, DBB valves are a game-changer in the valve industry, offering substantial savings in weight, space, and installation time, improving environmental safety, providing crucial safety features for maintenance, and boasting versatility with added functions.
Industries and Applications for DBB Valves
Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valves, known for their versatility and safety features, find applications across a wide range of industries. In the oil and gas industry, for example, DBB valves are essential for isolation during maintenance or for the safe release of gases and liquids. Similarly, in the petrochemical industry, they are used for their effective isolating capabilities, particularly when handling hazardous fluids. The chemical industry also benefits from the use of DBB valves, where they ensure safe containment and controlled release of aggressive chemicals. In power generation plants, DBB valves are often used to manage high-pressure systems safely. They also find applications in water treatment plants, where they assist in regulating flow and isolating sections for maintenance. In summary, DBB valves are utilized wherever there is a need for a compact solution that offers double isolation and a bleed function to ensure safe operation.
DBB Valves Vs. DIB Valve
- Double Block and Bleed Valve (DBB): A DBB valve essentially has two sealing surfaces or mechanisms (blocks) that can isolate the flow of the medium (like gas or liquid). The ‘bleed’ function is an additional feature that allows for the pressure trapped between these two blocks to be safely vented or ‘bled’ out, if necessary. This is usually achieved through a vent or drain valve in the valve body’s cavity. DBB valves are used in critical applications where leakage can have serious consequences, and it is necessary to ensure the complete isolation of the medium.
- Double Isolation and Bleed Valve (DIB): A DIB valve also has two sealing surfaces, similar to a DBB valve, but with an important difference. In a DIB valve, both of these sealing surfaces or mechanisms are designed to be bidirectional, i.e., they can block the flow of the medium from either direction (upstream or downstream). The ‘bleed’ function is the same as in a DBB valve – it allows the pressure trapped between the two blocks to be safely vented out. This bidirectional feature makes DIB valves suitable for applications where the flow direction might change or where isolation is required on both sides of the valve.
Summary
Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valves, available in Modular and Integral designs, are critical in various industries, including oil and gas, petrochemicals, and power generation. These valves provide dual isolation and a bleed function, ensuring complete shut-off of fluid flow and enhanced safety during maintenance tasks. The selection of a suitable DBB valve depends on the nature of the application, the type of medium being controlled, and the operational conditions. DBB valves offer significant benefits such as space and weight savings, environmental safety, maintenance safety, and added functionality. They differ from Double Isolation and Bleed (DIB) valves in that DIB valves provide bidirectional isolation.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.